SE 2 - Software Processes
Software Process
Software Process (Software methodologies)
- Set of related activities that leads to the production of the computer
- Development of the software from the scratch or modifing an existing system
What is UML - Unified Modeling Language
- Usage:
- It's a drawing language for softwares (diagrams)
- No codes
- Give an idea how software works
- What it does
- What are the inputs, outputs and processes
- Helps to write code better
- Saves time and mistakes later
| 📘 Name | 🤔 What It Shows | 🧸 Simple Example |
|---|---|---|
| Class Diagram | The parts (like blueprints) of the software | Like showing each LEGO house’s shape |
| Use Case Diagram | What users can do | Like showing what buttons a game has |
| Sequence Diagram | Who talks to who and when | Like a comic strip of people talking |
| Activity Diagram | Steps in doing something | Like showing how to make a sandwich 🥪 |
| State Diagram | How something changes over time | Like a traffic light: red → green → yellow 🚦 |
Fundamental SE Processes
Common for all software processes
- Specification
- Defining what the system should do
- Fucntionality of the software
- Consraints on its operations
- Design and imlimentattion
- Define organization of the system [ sructured / object oriented ]
- Impliment the system -- > put the system in use
- Verication and Validation
- Confirm the software specification meets the customer needs.
- Evolution / Maintance
- Change the system according to changing customer needs
Software Process Description
- Products / outputs
- Outcome of process activity after testing
- Roles / actors
- Who is responsible
- Pre-conditions
- What must be true before testing
- Past-conditions
- What must be true after teesting
- Input
- What produce after testing
Examples for these processes:

Software Process Types
- Plan-driven Processes
- Activities are planned
- Progressed measured against plan
- Used for formal documentation
- Agile Development
- Incrimental Planing
- Easy to change requirements
- Flexible - less formal
What is "coping with change"?
- Designing, developing and managing the system for changing requuirements, technology and context by minimizing cost and effort.
Two approches to reduce rework cost
- Change anticipation
- Developer thinks the system should change in future, so developer build it in a way to update easily when those requirements appear.
- Change tolarance
- Even if something change without expecting, but the system can handle it without any break-down.
Two ways of coping with changes
- System Prototyping - simple model
- Throw-away prototyping
- Source code of prototyping is not use after preview prototype
- Evolutionary prototype
- Edit the source code for whole system
- Throw-away prototyping
- Incrimental Delivery - develop piece by piece
1. Waterfall Model
- Requirement Analysis & Definition
- System & Software Design
- Implimantation
- Testing
- Deployment
- Operation and maintance
| Features | Problems |
|---|---|
| Simple and easy to undersstand | Late client feedback |
| Clear stucture and well documentation | Inflexiable for evolution |
| Well define stages | Risk of errors |
| Estaminishing final cost and date | Not ideal for larger projects |

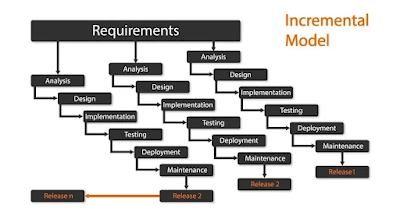
2. Incremental Develompent
- Develop the system parts by parts
- Get user feedback for each small developed part
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Lower risk | No completed documnetations |
| Flexiable to change | Putting parts together is tricky |
| User can view every stage | Not suaitable for complex systems |
| Devolopers can focused on small parts at once | Later parts will not match as ealier parts |
3. Reuse - oriented Software Engineering
- Use existing code for your project.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Faster to build | Parts may not be perfectly match |
| Save money and time | Hard to modify some codes |
| Less bugs | Don't know how it was built |
| Easy to maintaince | Legal issues of copyright |

4. Rational Unified Process (RUP)
- Setup by step processing the system
- It has 4 big phases
- Inception - what to build
- Eloboration - how we build it
- Constuction - let's build it
- Transition - give some one to test and fix broken things
- Not getting feedback from user to every developed part
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Has a clear 4 stages | Not suatable for small projects |
| Find problem ealry by planning and testing | Need a lot of plans and documents |
| Use for big systems to safe and clean work | Bit slow and expensive if over-used |
| Support updates in development | hard to adjust faster moving projects |

5.Boehm's Spiral Model
- Plan - check - build - test , repeat these steps in a every circle.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Good for risky projects | Need experts |
| Find problem ealry | No specific documents |
| Flexiable to change | Gets a lot of time |
| User gives feedback often | Expensive |

Source: Software Engineering — Software Process and Software Process Models (Part 2) | by Omar Elgabry | Medium
Comments
Post a Comment